Africa
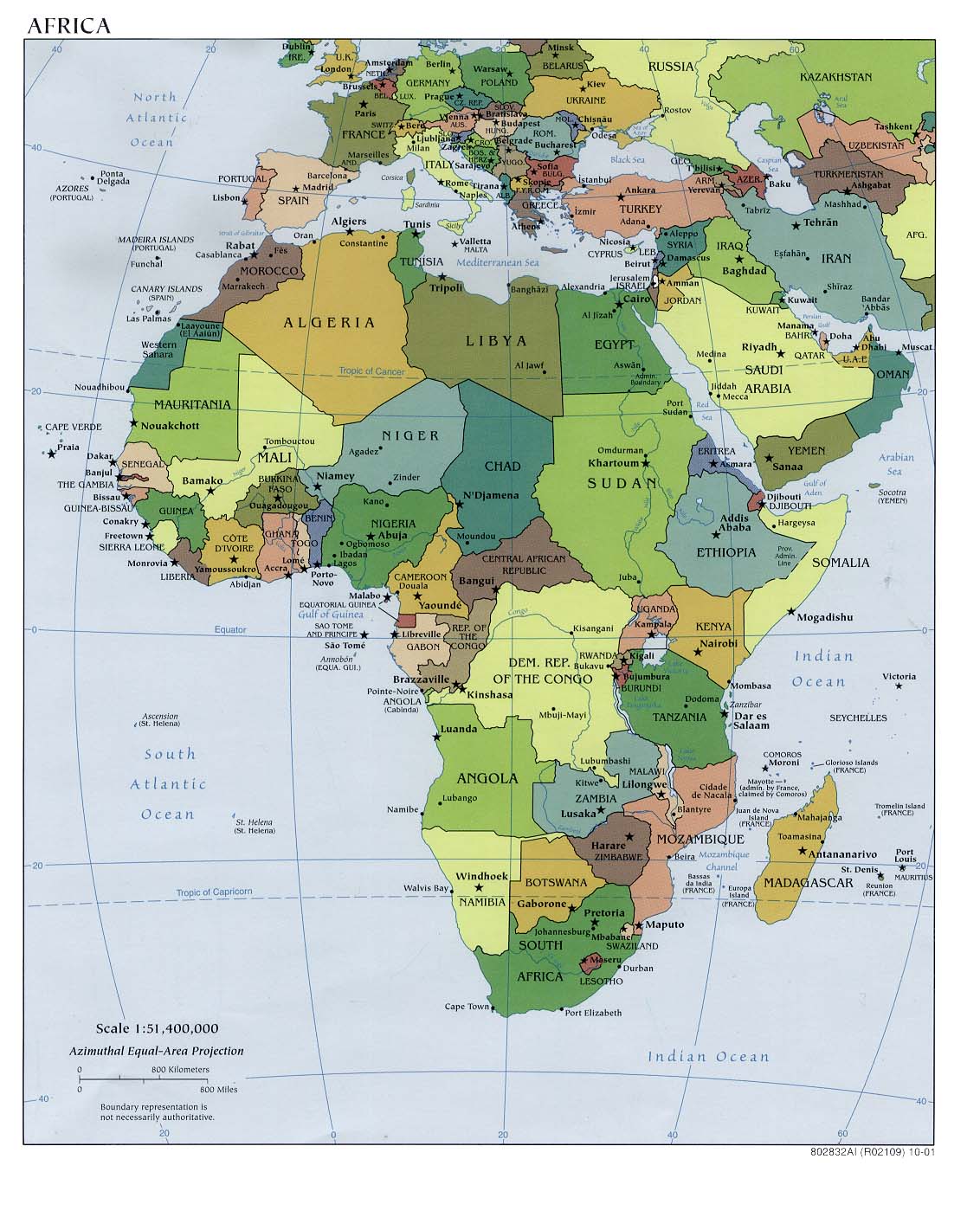
Africa is the world's second-largest and second most-populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² (11.7 million sq mi) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area. With 1.0 billion people (as of 2009, see table) in 61 territories, it accounts for about 14.72% of the world's human population.
The continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, both the Suez Canal and the Red Sea along the Sinai Peninsula to the northeast, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The continent has 54 sovereign states, including Madagascar, various island groups, and the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, a member state of the African Union whose statehood is disputed by Morocco.
Africa, particularly central eastern Africa, is widely regarded within the scientific community to be the origin of humans and the Hominidae clade (great apes), as evidenced by the discovery of the earliest hominids and their ancestors, as well as later ones that have been dated to around seven million years ago – including Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Australopithecus africanus, A. afarensis, Homo erectus, H. habilis and H. ergaster – with the earliest Homo sapiens (modern human) found in Ethiopia being dated to circa 200,000 years ago.
Geography of Africa
A composite satellite image of Africa (centre) with North America (left) and Eurasia (right) to scale
Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest landmass of the Earth. Separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea, it is joined to Asia at its northeast extremity by the Isthmus of Suez (transected by the Suez Canal), 163 km (101 miles) wide. (Geopolitically, Egypt's Sinai Peninsula east of the Suez Canal is often considered part of Africa, as well.)
Biomes of Africa
From the most northerly point, Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia (37°21' N), to the most southerly point, Cape Agulhas in South Africa (34°51'15" S), is a distance of approximately 8,000 km (5,000 miles); from Cape Verde, 17°33'22" W, the westernmost point, to Ras Hafun in Somalia, 51°27'52" E, the most easterly projection, is a distance of approximately 7,400 km (4,600 miles). The coastline is 26,000 km (16,100 miles) long, and the absence of deep indentations of the shore is illustrated by the fact that Europe, which covers only 10,400,000 km² (4,010,000 square miles) – about a third of the surface of Africa – has a coastline of 32,000 km (19,800 miles).
Africa's largest country is Sudan, and its smallest country is the Seychelles, an archipelago off the east coast.The smallest nation on the continental mainland is The Gambia.
According to the ancient Romans, Africa lay to the west of Egypt, while "Asia" was used to refer to Anatolia and lands to the east. A definite line was drawn between the two continents by the geographer Ptolemy (85–165 AD), indicating Alexandria along the Prime Meridian and making the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea the boundary between Asia and Africa. As Europeans came to understand the real extent of the continent, the idea of Africa expanded with their knowledge.
Geologically, Africa includes the Arabian Peninsula; the Zagros Mountains of Iran and the Anatolian Plateau of Turkey mark where the African Plate collided with Eurasia. The Afrotropic ecozone and the Saharo-Arabian desert to its north unite the region biogeographically, and the Afro-Asiatic language family unites the north linguistically.
Climate
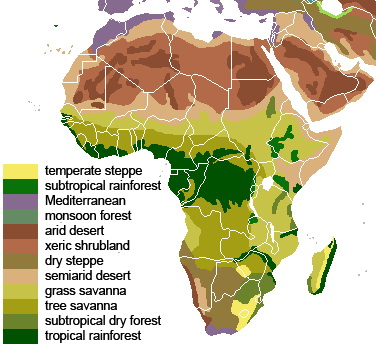
The climate of Africa ranges from tropical to subarctic on its highest peaks. Its northern half is primarily desert or arid, while its central and southern areas contain both savanna plains and very dense jungle (rainforest) regions. In between, there is a convergence where vegetation patterns such as sahel, and steppe dominate.
Fauna
Main article: Fauna of Africa
Savanna at Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania.
Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of wild animal populations and diversity, with wild populations of large carnivores (such as lions, hyenas, and cheetahs) and herbivores (such as buffalo, deer, elephants, camels, and giraffes) ranging freely on primarily open non-private plains. It is also home to a variety of "jungle" animals including snakes and primates and aquatic life such as crocodiles and amphibians. Africa also has the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna.
Ecology
Deforestation is affecting Africa at twice the world rate, according to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Some sources claim that deforestation has already wiped out roughly 90% of West Africa's original forests. Since the arrival of humans 2000 years ago, Madagascar has lost more than 90% of its original forest.About 65% of Africa's agricultural land suffers from soil degradation.
Culture of Africa
Some aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practiced in recent years as a result of years of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalourise African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of Vodou and other forms of spirituality. In recent years, traditional African culture has become synonymous with rural poverty and subsistence farming.
Visual art and architecture
African art and architecture reflect the diversity of African cultures. The oldest existing examples of art from Africa are 82,000-year-old beads made from Nassarius shells that were found in the Aterian levels at Grotte des Pigeons, Taforalt, Morocco.The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt was the world's tallest structure for 4,000 years, until the completion of Lincoln Cathedral around the year 1300. The stone ruins of Great Zimbabwe are also noteworthy for their architecture, and the complexity of monolithic churches at Lalibela, Ethiopia, of which the Church of Saint George is representative.
A street musician performing in South Africa
Music of Africa
Egypt has long been a cultural focus of the Arab world, while remembrance of the rhythms of sub-Saharan Africa, in particular West Africa, was transmitted through the Atlantic slave trade to modern samba, blues, jazz, reggae, hip hop, and rock. The 1950s through the 1970s saw a conglomeration of these various styles with the popularization of Afrobeat and Highlife music. Modern music of the continent includes the highly complex choral singing of southern Africa and the dance rhythms of the musical genre of soukous, dominated by the music of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Indigenous musical and dance traditions of Africa are maintained by oral traditions, and they are distinct from the music and dance styles of North Africa and Southern Africa. Arab influences are visible in North African music and dance and, in Southern Africa, Western influences are apparent due to colonisation.
Sports
Fifty-three African countries have football (soccer) teams in the Confederation of African Football, while Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, and Ghana have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so. According to FIFA ranking, Egypt currently has the best soccer team in Africa. Their team has won the African Cup 7 times, and a record-making 3 times in a row.
Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa and Zimbabwe have Test status, while Kenya is the leading non-test team in One-Day International cricket and has attained permanent One-Day International status. The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup. Morocco in northern Africa has also hosted the 2002 Morocco Cup, but the national team has never qualified for a major tournament. Rugby is a popular sport in South Africa and Namibia.
Religion
The Great Mosque of Kairouan, erected in 670, is the oldest mosque in North Africa, Kairouan, Tunisia.
Main article: Religion in Africa Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are too sensitive a topic for governments with mixed populations.According to the World Book Encyclopedia, Islam is the largest religion in Africa, followed by Christianity. According to Encyclopedia Britannica, 45% of the population are Muslims, 40% are Christians and less than 15% continue to follow traditional African religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Baha'i, or have beliefs from the Judaic tradition. Examples of African Jews are the Beta Israel, Lemba peoples and the Abayudaya of Eastern Uganda. There is also a small minority of Africans who are non-religious.
